Discover how the initial symptoms of diabetes manifest and learn how proper control of this disease aids in oral health.
Diabetes is a condition caused by insufficient production or poor absorption of insulin, a hormone that regulates blood glucose and ensures energy for the body.
Therefore, it is of utmost importance to be aware of the risk factors and symptoms of the disease. Interestingly, the first signs can appear in the mouth.
What are the signs of diabetes that appear in the mouth?
Diabetes affects blood sugar control in the body, which reflects on blood circulation and reduces salivary flow. This results in a drier mouth and changes in the pH of saliva, thus losing its protective effect.
Consequently, the oral cavity becomes more prone to infections such as periodontitis, in addition to a higher susceptibility to the action of herpes virus and candida.
Experts say that diabetes may not show obvious symptoms at the beginning. However, some signs manifest in the mouth and deserve your attention:
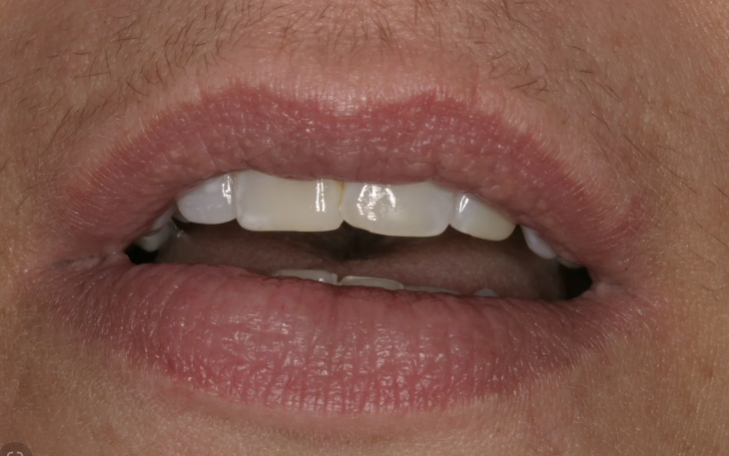
1) Dry Mouth. Dryness of the mouth, also known as xerostomia, is a consequence of reduced saliva production in response to increased blood sugar levels.
2) Red and Sensitive Gums. The increased blood sugar level facilitates the proliferation of bacteria in the mouth, which can result in red, sensitive, and painful gums, and may even bleed during brushing.
3) Tooth Loss. Teeth may be lost more easily when diabetes is uncontrolled. This is due to a higher propensity for periodontal diseases, cavities, and other oral infections.
4) Increased Sugar in Saliva. The elevation of glucose levels in saliva creates a favourable environment for the development of bacteria, increasing the likelihood of cavities and oral infections.
5) Bad Breath. Ketone breath, a smell of rotting fruit, is common when the disease is uncontrolled, and blood sugar levels are very high or very low. It is a vital indicator for the diagnosis of diabetes, especially when associated with other symptoms, such as increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue.
6) Delayed Healing. Diabetes can compromise the body's ability to recover from injuries, which can result in complications after dental procedures.
7) Mouth Ulcers. The presence of ulcers and sores in the mouth is more common among diabetic patients, especially when the disease is poorly managed.
Given these symptoms, patients with diabetes should make regular visits to the dentist, in addition to maintaining proper oral hygiene.
Early identification and correct treatment of the disease are essential for maintaining the oral and overall health of the patient.
Source Dagens.com